PyCharm Professional
The official documentation on configuring a docker interpreter is pretty complete, but there are caveats. Below, you will find an improved configuration guide helping you to set up the runtime quickly.
The guide tested with PyCharm 2023.1.4 Professional.
Note
If you have a different version of PyCharm, we cannot guarantee that the settings will work and match the screenshots.
Project Preparation
Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/insight-platform/Savant.git
Copy and rename the template (let’s name the new project
my-module):cp -r Savant/samples/template my-module
Start the IDE and create a new project in the
my-moduledirectory.When creating a project, select the system Python interpreter
Setting Up The Interpreter for the Module
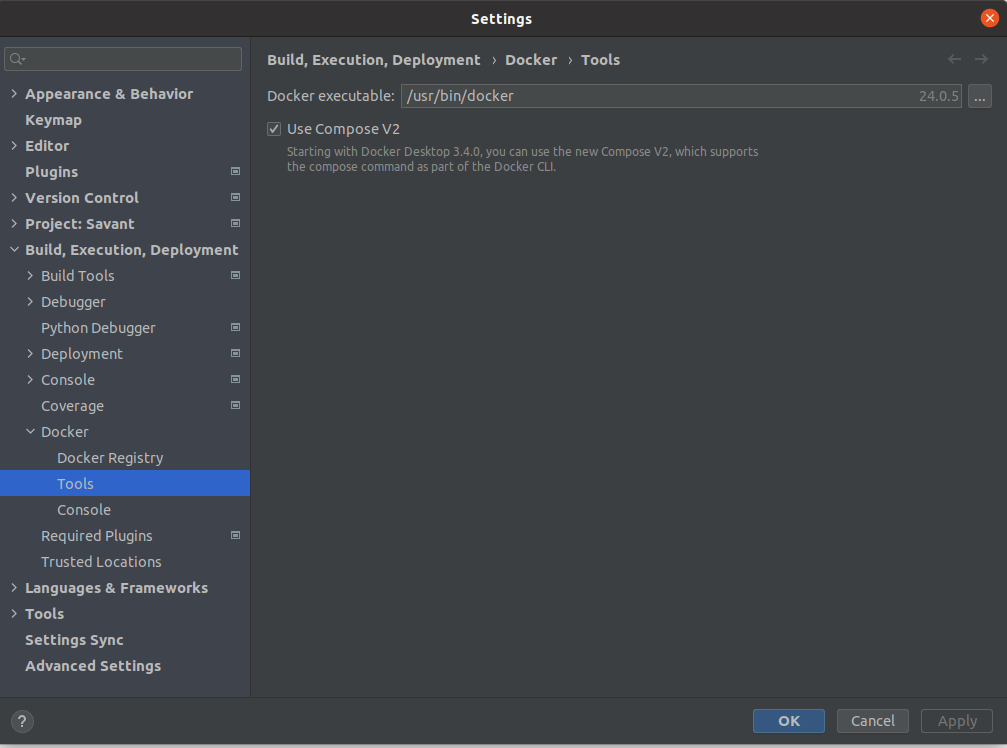
Open the project settings with File > Settings … or Ctrl+Alt+S. Set Use compose V2 in Build, Execution,Deployment > Docker > Tools
Open the project settings with File > Settings … or Ctrl+Alt+S.
Select Project: my-module > Python Interpreter section.
Add a new Python Interpreter by clicking the Add Interpreter, and selecting On Docker Compose…:
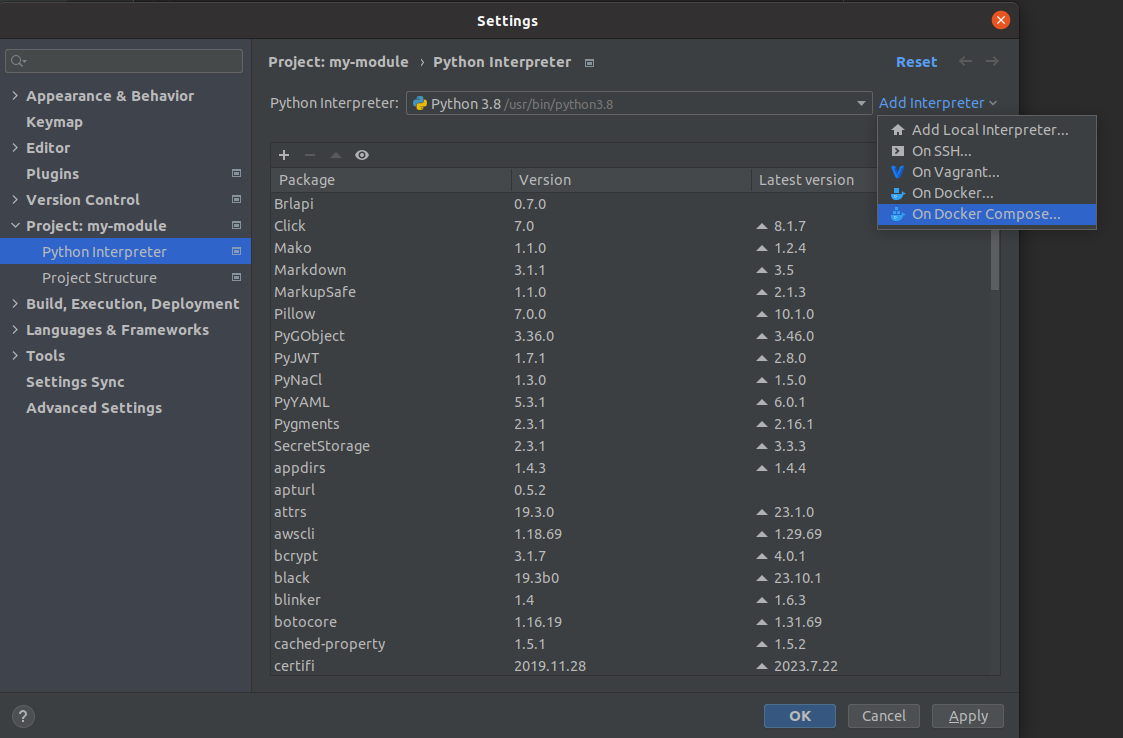
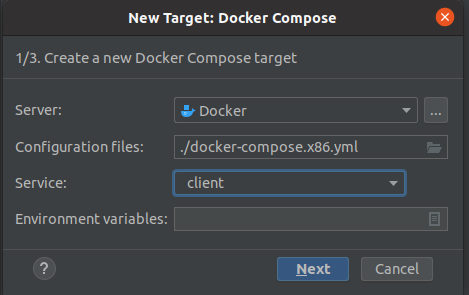
In the modal window:
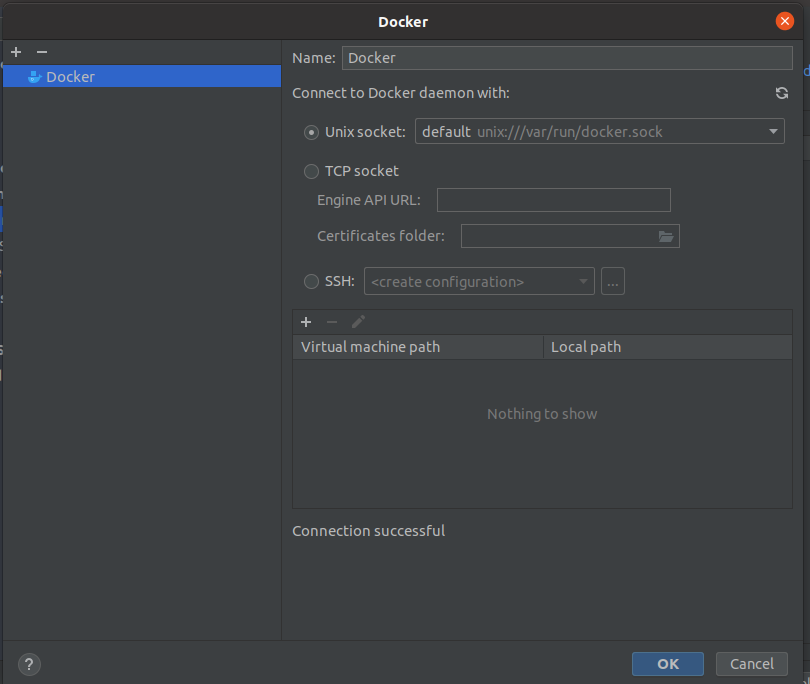
Click on the three dots under Server and set up access to the docker service
Select Configuration file:
docker-compose.x86.yml(docker-compose.l4t.ymlfor Jetson) and select the service module: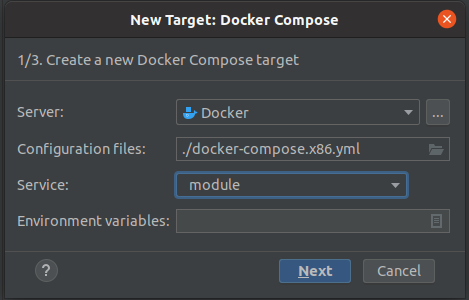
Click Next button, make sure docker build is successful and then again click Next button.
Keep the default python interpreter (python3) and click Create:
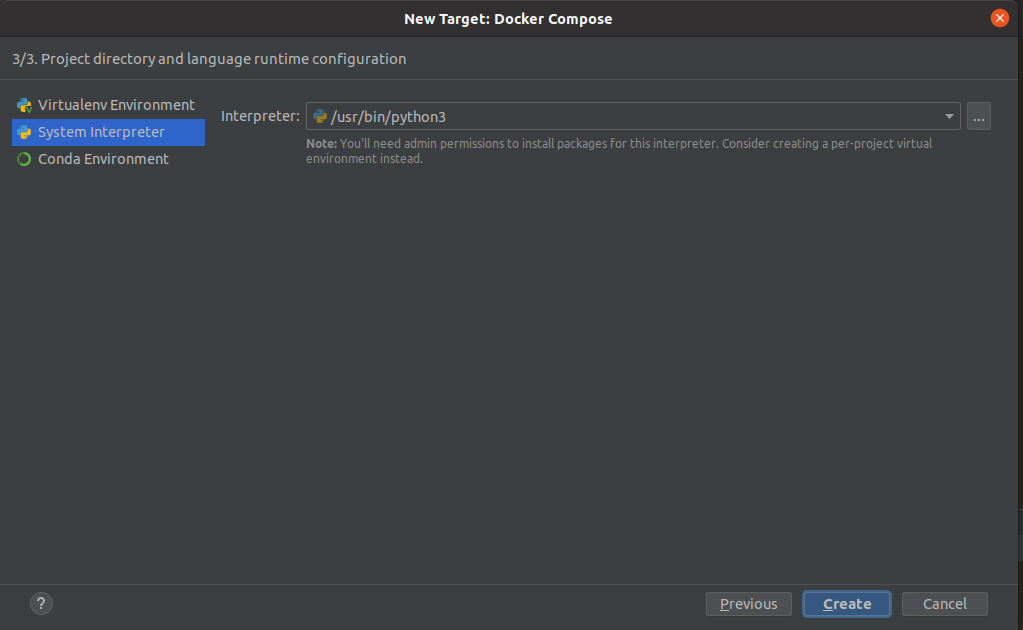
Make sure that the
savantpackage is in the package list, click OK: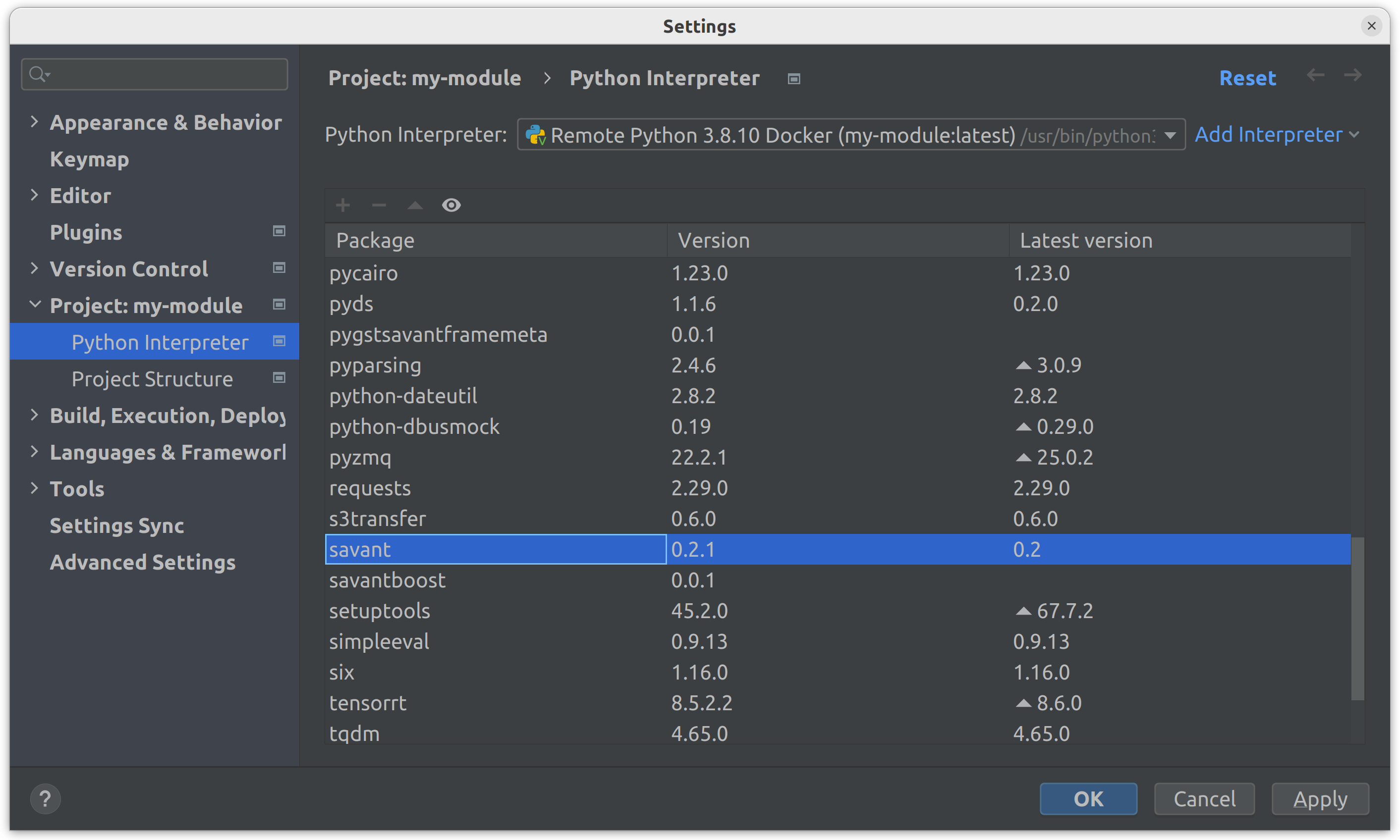
Setting Up The Interpreter for the Client
Configure Module Run
The module/run.py file is the entrypoint of the module, let’s configure the launch command for the script.
Open the
module/run.pyscriptRight click of mouse on the tab
module/run.pyand select Modify Run Configuration in “”More Run/Debug: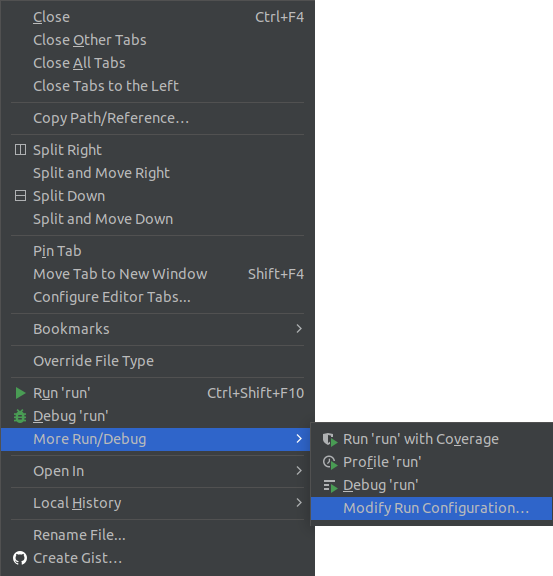
In the Environment section add
PYTHONPATH=/opt/savant(PyCharm rewritesPYTHONPATH), select Docker compose(module) interpreter. If you used a custom Dockerfile, you need to setup --build modulein Docker Compose > Command and options.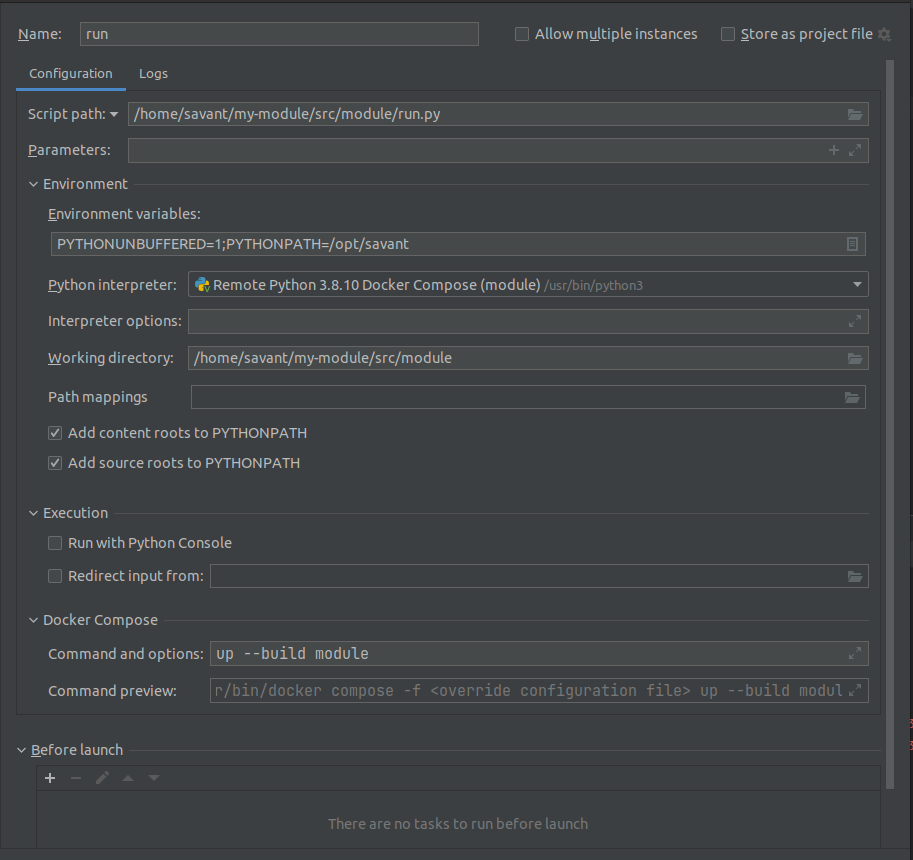
Launch the module by selecting Run ‘run’ or with the hotkey Ctrl+Shift+F10:
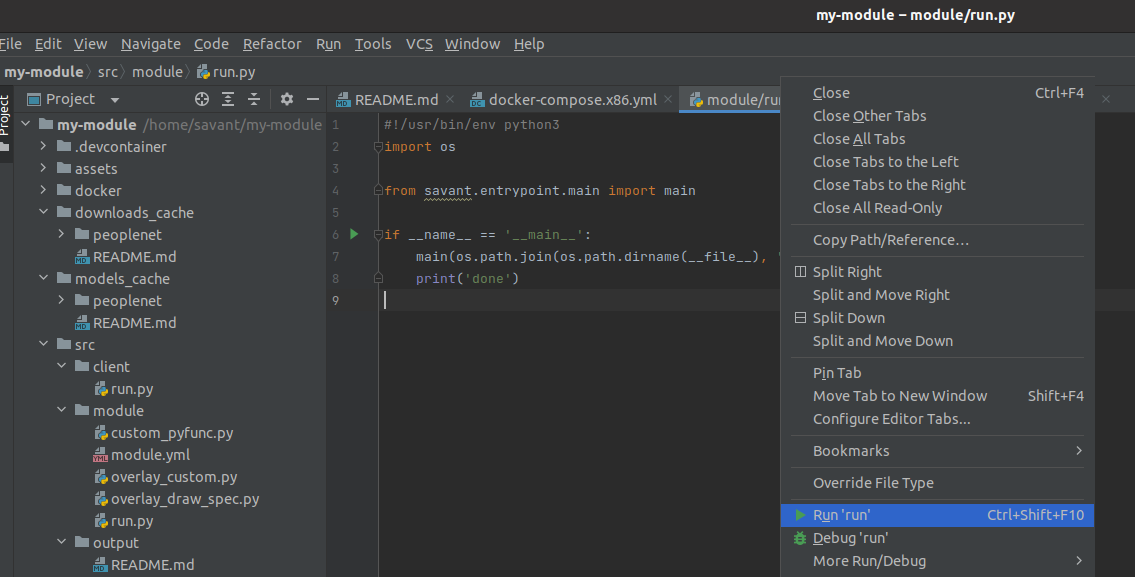
You may see various GStreamer error messages: it’s ok. At the end you will see the output
module status to ModuleStatus.RUNNING.:
Configure Client Run
The client/run.py This is a script that allows you to interact with the module by sending data and receiving results. Let’s configure the launch command for the script.
Open the
client/run.pyscriptRight click of mouse on the tab
client/run.pyand select Modify Run Configuration in “”More Run/Debug:
In the Environment section add
PYTHONPATH=/opt/savant(PyCharm rewritesPYTHONPATH) and select Docker compose(client) interpreter: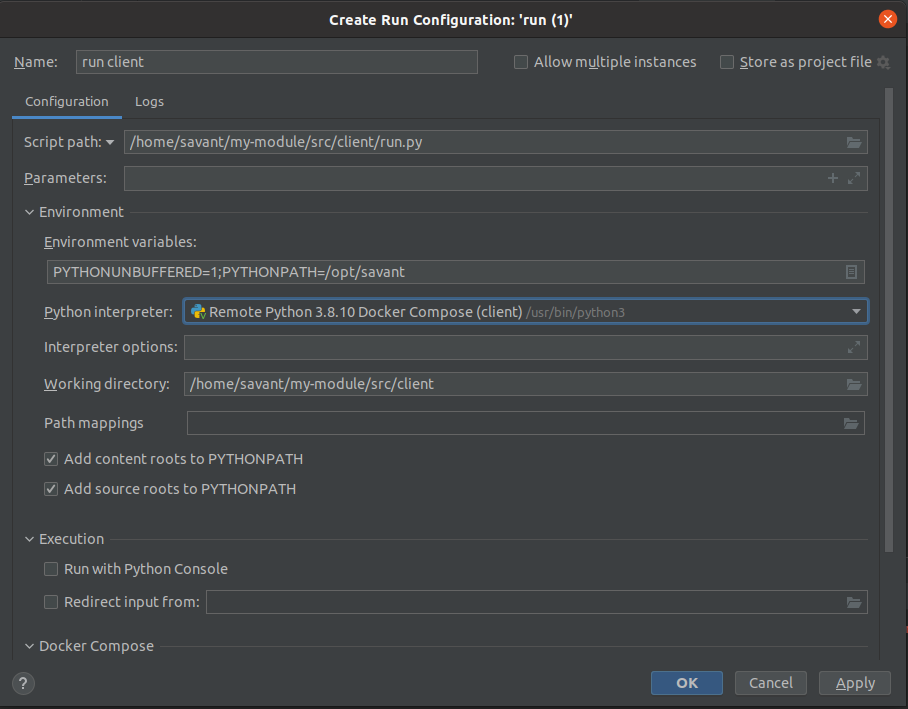
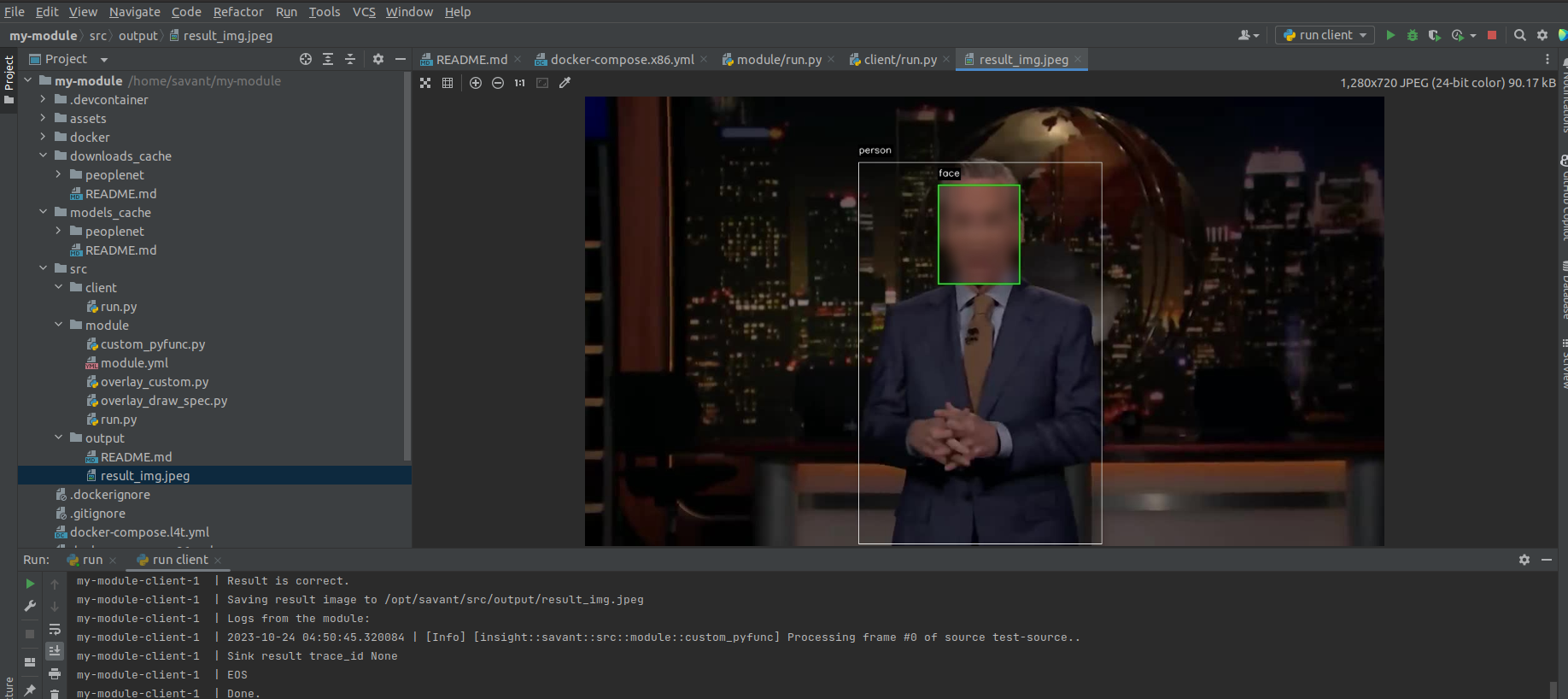
Launch the client script by selecting Run ‘run client’ or with the hotkey Ctrl+Shift+F10:
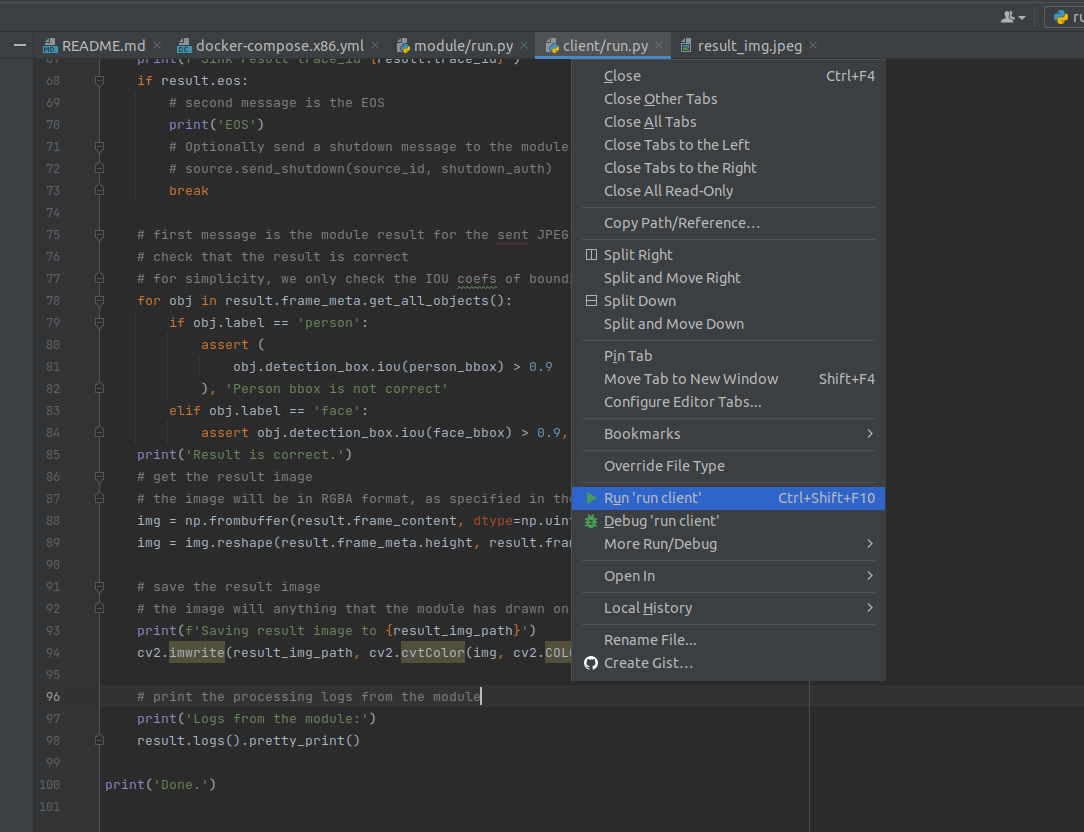
Check the results:
That’s it, the environment is set up. Now you are ready to develop your own pipeline. See the next section to find out how.
Update Runtime On Container Change
Changes to the Dockerfile or the base image
If you used a custom Dockerfile you should check that the up --build module option is set in the Run configuration settings. If this option is set and you have made any changes to the Dockerfile or updated the base image, you don’t need to do anything else. At the next run a new image will be built and the container will be updated.

Adding new packages to requirements.txt
Once dependencies are added to the requirements.txt, they will be automatically installed when building a new image.
However, PyCharm does not automatically detect newly installed packages in the Docker container. The PyCharm will update the skeleton at the next startup or you can manually scan for new packages. To do this, you need to open the Settings and look for Rescan, then navigate to Plugins > Python > Rescan Available Python Modules and Packages and set the hotkey (e.g., Alt+R):
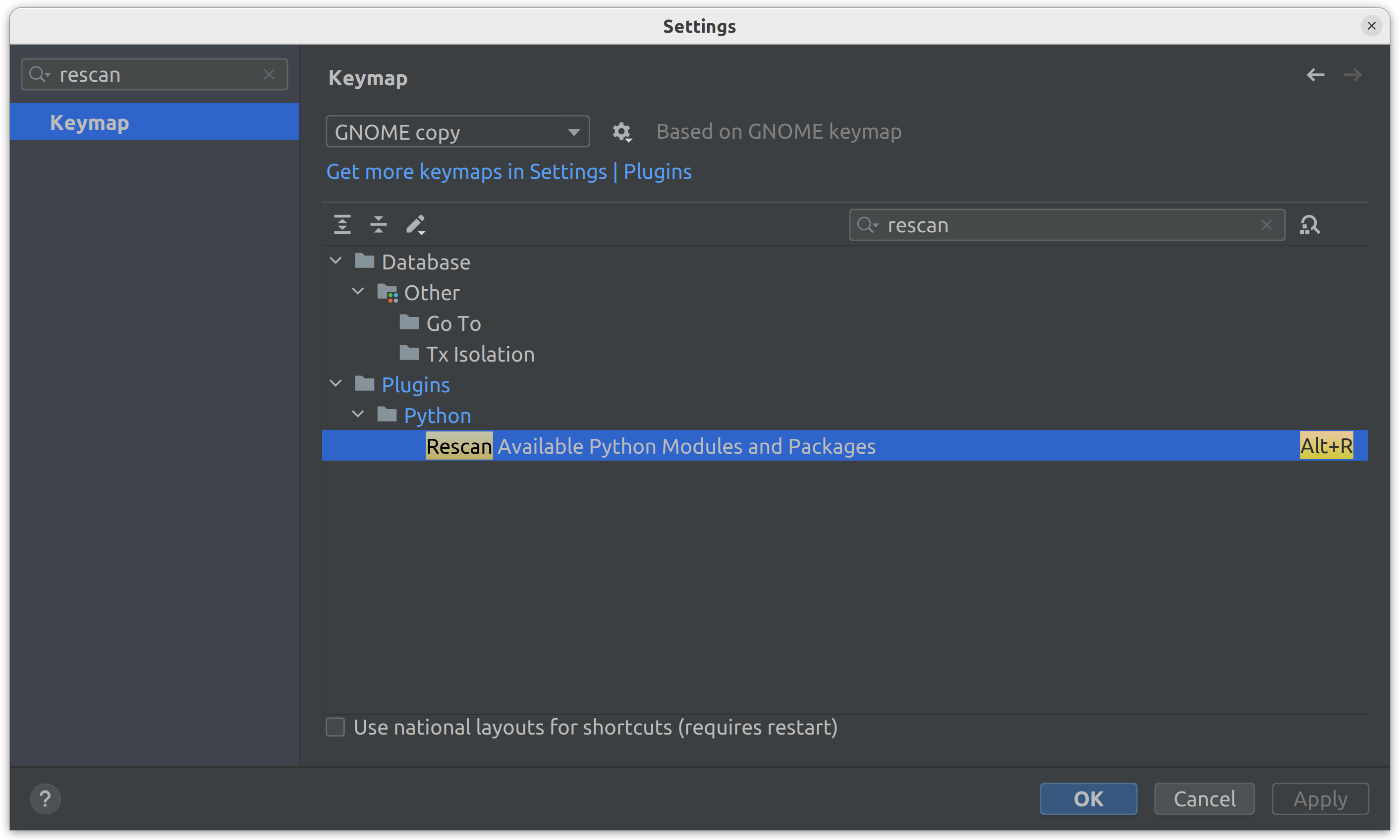
After adding a new package to the requirements.txt, simply press the specified hotkey to rebuild the image and update the packages.
In the following sections, you will find additional details on module development.